Schulpflicht: How Austria pioneered mandatory schooling for all
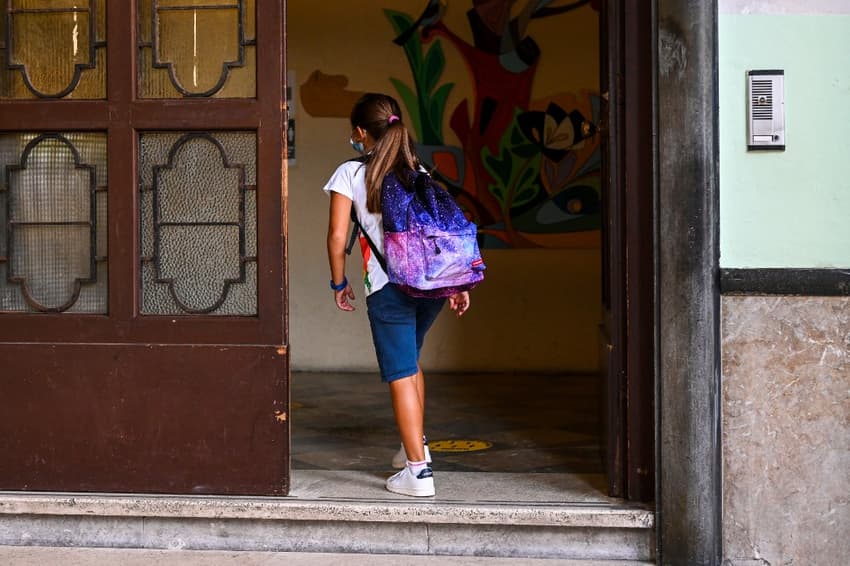
Schoolchildren in Vienna, Lower Austria and Burgenland went back to the books last week, with the rest of the country to follow next week. Parents and children in both Austria and around the world can thank – or blame – one Austrian empress for that.
Maria Theresa was the only woman to ever rule Austria as monarch, acceding in 1740 at age 23 to the throne of a financially broke state – before having to immediately fight a war to retain her crown. She went on to have 16 children – yes, you read that right – 16, including doomed French queen Marie Antoinette.
Although her 40-year reign was punctuated by state crises, an active family life, and quite a bit of state and educational reform – her most lasting legacy is one seen around the world this day – the Schulpflicht, or “mandatory schooling”.
Maria Theresa’s Austria wasn’t the first place in Europe or the world to pioneer mandatory schooling – but along with the German state of Prussia at the time, it was the among the first to do it on the scale it did. Late in her reign, Maria Theresa decreed that all children in the Hapsburg empire – which included Austria, Hungary, Croatia and bits of what is now Italy, Czechia, Slovakia, and Poland – attend state-sponsored education from age six to twelve.
The order applied to all children regardless of background, mother tongue, or gender. Both girls and boys were to attend school, regardless of whether they were the children of peasants and farmers or born to Austrian nobles and aristocrats.
A multilingual empire at the time, children who were Maria Theresa’s subjects were first educated in their native language before receiving instruction in German later on.
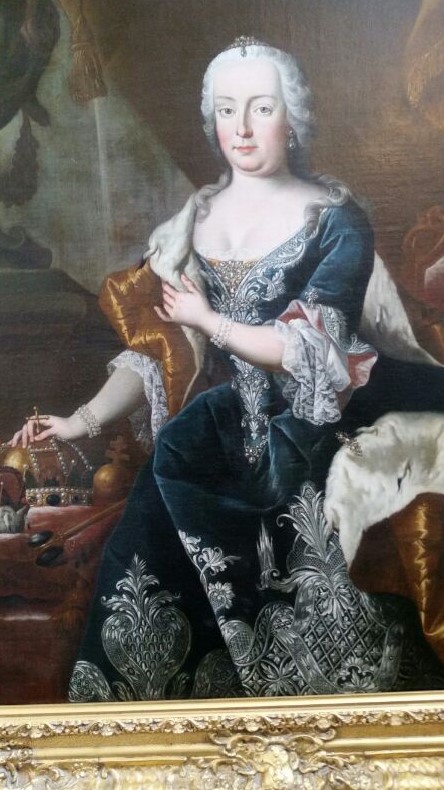

Austrian Habsburg Empress Maria Theresa ruled from 1740 to 1780 - and introduced the first public schools to Austria - one of the first in the world to do so. Austrians continue to celebrate Maria Theresa through sculptures and portraits, including this one at Schönbrunn Palace. Photo: Aaron Burnett
Up until then, education had been mainly a luxury of the elite, and often only possible through either church institutions or private tutors. Although rich families who could afford tutors were still allowed to have their children educated this way, Maria Theresa’s network of secular public schools and teacher recruitment changed education in Austria to something more like what we’re used to today – and other countries eventually followed suit.
She was also ruthless about enforcing her policy. Many peasants initially protested having to send their children to school, arguing that they needed their children’s help tilling the fields at home. She responded by arresting those opposed, including those who kept their children home from school.
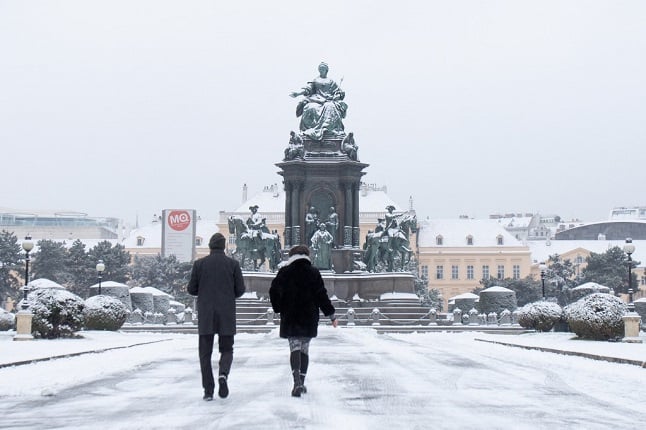

People walk in front of the snow-covered memorial of Empress Maria Theresa (1717-1780) in Vienna on December 3, 2020. (Photo by ALEX HALADA / AFP)
Her policy saw Austrian literacy rates increase, although some of biggest gains in school attendance were seen in the years following her death in 1780. At that time, an estimated 40 percent of Austrian children regularly attended school, despite it being mandatory. By the early 1800s, this had jumped to a near universal 94 percent.
READ ALSO: Four things foreigners in Austria need to know about the education system
Mandatory schooling in Austria today
Today, each child that is permanently resident in Austria and at least six years of age on September 1st of each year must attend school.
Nine years of primary schooling are compulsory, followed by three years at secondary school.
Every spring, parents of school-aged children in Austria will typically get a letter in the post requesting them to register their children for the upcoming school year at the school nearest their residence.
The exact timing of this letter can vary from state to state. In Vienna, it is typically sent out in March. If the parents want to send their kids to another school, they must make a request to the school inspector of the relevant district, contact a private school principal, or inform their regional school board that they intend to homeschool their kids.
READ ALSO: Reader question: Is home schooling legal in Austria
State support for supplies
In 2011, Austria added another feature to its education system that few other countries copy – state support for buying school supplies. Every year, parents with school-aged children are entitled to a €105.80 payment from the government – per child – to help them pay for paper, pens, and other supplies their kids will need for school. No special application is necessary, as the payments come out alongside Familienbeihilfe subsidies in August of each year.
READ ALSO: ‘Schulstartgeld’: How much are Austria’s ‘starting school’ grants worth?
Comments
See Also
Maria Theresa was the only woman to ever rule Austria as monarch, acceding in 1740 at age 23 to the throne of a financially broke state – before having to immediately fight a war to retain her crown. She went on to have 16 children – yes, you read that right – 16, including doomed French queen Marie Antoinette.
Although her 40-year reign was punctuated by state crises, an active family life, and quite a bit of state and educational reform – her most lasting legacy is one seen around the world this day – the Schulpflicht, or “mandatory schooling”.
Maria Theresa’s Austria wasn’t the first place in Europe or the world to pioneer mandatory schooling – but along with the German state of Prussia at the time, it was the among the first to do it on the scale it did. Late in her reign, Maria Theresa decreed that all children in the Hapsburg empire – which included Austria, Hungary, Croatia and bits of what is now Italy, Czechia, Slovakia, and Poland – attend state-sponsored education from age six to twelve.
The order applied to all children regardless of background, mother tongue, or gender. Both girls and boys were to attend school, regardless of whether they were the children of peasants and farmers or born to Austrian nobles and aristocrats.
A multilingual empire at the time, children who were Maria Theresa’s subjects were first educated in their native language before receiving instruction in German later on.

Up until then, education had been mainly a luxury of the elite, and often only possible through either church institutions or private tutors. Although rich families who could afford tutors were still allowed to have their children educated this way, Maria Theresa’s network of secular public schools and teacher recruitment changed education in Austria to something more like what we’re used to today – and other countries eventually followed suit.
She was also ruthless about enforcing her policy. Many peasants initially protested having to send their children to school, arguing that they needed their children’s help tilling the fields at home. She responded by arresting those opposed, including those who kept their children home from school.

Her policy saw Austrian literacy rates increase, although some of biggest gains in school attendance were seen in the years following her death in 1780. At that time, an estimated 40 percent of Austrian children regularly attended school, despite it being mandatory. By the early 1800s, this had jumped to a near universal 94 percent.
READ ALSO: Four things foreigners in Austria need to know about the education system
Mandatory schooling in Austria today
Today, each child that is permanently resident in Austria and at least six years of age on September 1st of each year must attend school.
Nine years of primary schooling are compulsory, followed by three years at secondary school.
Every spring, parents of school-aged children in Austria will typically get a letter in the post requesting them to register their children for the upcoming school year at the school nearest their residence.
The exact timing of this letter can vary from state to state. In Vienna, it is typically sent out in March. If the parents want to send their kids to another school, they must make a request to the school inspector of the relevant district, contact a private school principal, or inform their regional school board that they intend to homeschool their kids.
READ ALSO: Reader question: Is home schooling legal in Austria
State support for supplies
In 2011, Austria added another feature to its education system that few other countries copy – state support for buying school supplies. Every year, parents with school-aged children are entitled to a €105.80 payment from the government – per child – to help them pay for paper, pens, and other supplies their kids will need for school. No special application is necessary, as the payments come out alongside Familienbeihilfe subsidies in August of each year.
READ ALSO: ‘Schulstartgeld’: How much are Austria’s ‘starting school’ grants worth?
Join the conversation in our comments section below. Share your own views and experience and if you have a question or suggestion for our journalists then email us at [email protected].
Please keep comments civil, constructive and on topic – and make sure to read our terms of use before getting involved.
Please log in here to leave a comment.